As Founder & Managing Director of Ambassador Technologies, Richard provides strategic leadership and support for all clients.
- Science stem activities for preschool
- Good science fair projects for 5th graders
- Science fair volcano
- Skittles science fair project
- Easy science fair projects
- What is stem science
- Engineering science fair projects
- Science projects for class 8
- Science project technology and toy
- Steam science projects
- What is a stem professional
- 100 science words with meaning
- Science project online
- Science and technology
- The academy of motion picture arts and sciences
- Material definition science
- Wind energy science projects for students
- Steam lesson ideas
- Science fair projects
- Life science science fair projects
- Why science is important for students
- Symbol meaning in science
- Science stem activities for kindergarten
- Earth science for stem
- Science project board
- Define biology in science
- Stem activities for 2 year olds
- Good science fair projects for 7th graders
- Bio science meaning
- Valentine stem activities
- Physics science fair projects
- Scientist definition
- Science and engineering
- Preschool science fair projects
- Easy stem projects
- Autumn stem activities
- Anatomy science fair projects
- Best science fair projects for 1st graders
- Best chemistry science fair projects
- Actuarial science course
- Stem life science
- Good science fair projects
- Windmill stem project
Ambassador Technologies
Cross-Border Business Development Services for Innovative Organizations
Nuclear chemistry
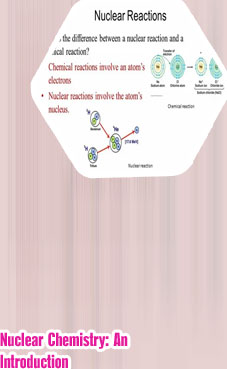
Department of Chemistry
Nuclear reactions differ from other chemical processes in one critical way: in a nuclear reaction, the identities of the elements change. In addition, nuclear reactions are often accompanied by the release of enormous amounts of energy, as much as a billion times more than the energy released by chemical reactions. Moreover, the yields and rates of a nuclear reaction are generally unaffected by changes in temperature, pressure, or the presence of a catalyst. Radioactivity definition chemistry Beta radiation: Produced by beta decay. Releases electrons, also known as beta particles.
Radioactivity definition physics
This activity takes 45-60 minutes Main navigation As a simple example of the energy associated with the strong nuclear force, consider the helium atom composed of two protons, two neutrons, and two electrons. The total mass of these six subatomic particles may be calculated as:
Types of radiationEdit
Occasionally, an atomic nucleus breaks apart into smaller pieces in a radioactive process called spontaneous fission (or fission). Typically, the daughter isotopes produced by fission are a varied mix of products, rather than a specific isotope as with alpha and beta particle emission. Often, fission produces excess neutrons that will sometimes be captured by other nuclei, possibly inducing additional radioactive events. Uranium-235 undergoes spontaneous fission to a small extent. One typical reaction is Chemistry Continue reading
Define nuclear chemistry
Registration coming soon. Food and Drink App: Radioactivity in Wines Nuclear energy is also harnessed to preserve our food.
